After all configuration ,you are ready to create objects in ADDS. Don't worry it's fun. Creating users , groups,computers and organizational unit is really very easy and an easy way to manage resources in ADDS. As previously mentioned that we create organizational units to place users, groups and computer so that we can manage and find an object in ADDS easily. so first of all I will let you know how to create an Organizational unit then groups and then users. Its not necessary that you will have to create groups first only then you can create users there is no such rule defined. why do we do it in that way so that you can manage because in an Enterprise Network it can be difficult for you to find an object. so let's get started with an OU
To create an organizational unit:
1. Open the Active Directory Users And Computers snap-in.
2. Right-click the Domain node or the OU node in which you want to add the new OU,
point to New, and then click Organizational Unit.
3. Type the name of the organizational unit.
Be sure to follow the naming conventions of your organization
Here is an image of creating OU in ADDS
As you see the image it's very easy . After that, you will see another window in which you need to mention the name of the Organizational Unit. On the bottom you will see an option that says "protect container from
accidental deletion" . It is not mandatory that you must select this option it's just a caution . If you have ever worked in an IT company when you are tired you are not really able to focus doing stuff. you may make mistake for instance if you delete an organizational unit you will loose all groups and user and other object placed in that organizational Unit. Again you will have to create all groups and user and other objects again you will have to assign them permission and access to resources . One group can be the member of other groups moreover all groups and users will lose their access to network resources . I am pretty sure your boss will take your class if you make such mistake so it's better to save you ass first. Here is an Image for
the option I explained about.
if this option is selected you will get an error message which I will show in the image .
If you intentionally want to delete an OU make sure this accidental protection option is not selected. Exactly in the same way you create groups and users and assign the name of Group. I strongly believe you can create group without any confusion. let's move and learn how to create a user, creating user is also very easy
just a little difference. I will upload an image so that you can easily can create user. when you create a user
you have to assign a First name,Initial ,last name and full name and user log on name too.
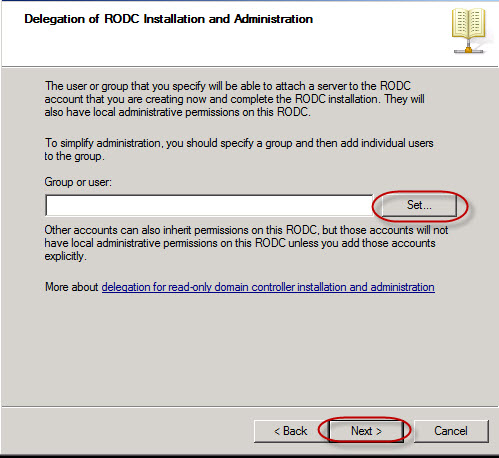
in next window you will be prompted to enter a strong password to enter. you will see many option for passwordto select. keep in mind you can not leave the password option blank . if you leave it blank you will get an error message "windows can not create the object Ankit Mr. Tyagi because:unable to update the password.The value provided for the password does not meet the length, complexity or history requirements of the domain. To know the password complexity requirements go to command prompt and run it as administrator and then type the command "
net accounts "
you will be able to see the password requirements. such as password minimum or maximum age ,password length. Account lockout duration in minutes, Account lockout threshold ,lockout observation windows in minutes. by default password meximum
age is set to 42 days. you can set password minimum and maximum age , Account lockout duration , Account lockout threshold and password complexity and other settings. At this time you are creating users
so let's continue with that after assigning the password you multiple option to select such as
1: User must change the password at next log on by default it is selected. when the user logs on to the computer for the first time he or she will be prompted to change the password.
2: User can not change the password. you will be given the password and you will not be able to change that password.
3: The next option would be password will never expired . whatever the password you have been given by
server administrator or member of the Admin group will never expire.
4: Account is disable . means you have the account but it is not enabled you can not log on to computer.

you have successfully created user now you must be thinking how to enable an account and how can we
reset the password for a user. I would like to tell you that there are two way to reset the password , a user
also can change the password if user knows the current password. Resetting password is totally diffrent.
If you are member of the group which has permission to reset the password they don't need your current
password. so let's get started with Enabling user account and resetting password. There are multiple ways
to view your Active Directory User you may chose any one of them
1:Start>Search program and files and type dsa.msc it's short command to view Active Directory user and
computer
2:Start>Administrative Tool> Active directory user and computers
once you have Active Directory User and Computers select the user you want to enable or reset the
password. If have not created any Organizational Unit or group you will see the user name appears
right hand pane,that's the default location . you will see there are a lot folders which have been assigned
name by windows itself. I will defiantly explain each container later. As you were going to learn how to
enable an account and how would you come to know that account has been disabled . you will see down
arrow on the user name. so let's enable an account. disable Account will look like as shown in image
as you can see the disabled account which has been indicated by an arrow. Simply right click and just
click on enable and consider your job done. After enabling the Account you need to reset password ,you
can reset the password a disable account as well it not necessary that account must enabled only then you
can reset password. if the account is disable you have an option on the of the password resetting box that
says unblock this account , all you need to do just to select that option.
And we are done with enabling account and resetting password now . It's time to know about the Group
I strongly believe that you know how to create a group however you might not aware of the Group type
which is really very important to understand. I will explain each and everything about the Groups .
Group: Groups are an important class object in ADDS. Most often are groups are used to assign permissions to network resources as it an easy way to manage and assign permissions.It would be
very difficult for you to assign permission to an individual user if you have to assign permission to 100
or more users probably you will have to spend whole day long to get it done. so you can say that groups
are center point of management from where you can assign read, write ,copy and modify permissions.
you might have seen that when you create a group you see multiple options to select. Most of the people
get confused about the type of Group in AD. There are only two types of group in Active Directory . So let's begin with creating group. Process is exactly same . The two types of groups are Security Groups and distribution Groups. You can use distribution groups to create e-mail distribution lists and
security groups to assign permissions to shared resources.
Distributions groups:Distribution groups can be used only with e-mail applications (such as
Exchange) to send e-mail to collections of users. Distribution groups
are not security-enabled, which means that they cannot be listed in
discretionary access control lists (DACLs). If you need a group for
controlling access to shared resources, create a security group.
Security groups: User rights are assigned to security groups to determine what members of
that group can do within the scope of a domain (or forest). User rights
are automatically assigned to some security groups at the time Active
Directory is installed to help administrators define a person's
administrative role in the domain. For example, a user who is added to
the Backup Operators group in Active Directory has the ability to backup
and restore files and directories located on each domain controller in
the domain.
This is possible because by default, the user rights back up files and directory and restore file and directory are automatically assigned to the Backup Operators group. Permissions should not be confused with user rights. Permissions are
assigned to the security group on the shared resource. Permissions
determine who can access the resource and the level of access, such as
Full Control. Some permissions set on domain objects are automatically
assigned to allow various levels of access to default security groups
such as the Account Operators group or the Domain Admins group. I know you are thinking that it is really to understand security and distribution group however it is not that much difficult . May be you need to read
about groups one more time. when you install active directory multiple groups are created automatically
such as Administrator Group, Back up operator Group, Account operator, power operator Group, Network Group etc. when your server is a domain controller more Group are added such domain admin
admin, schema Admin . If your domain controller is the domain in the forest then you will see more group.
1:Start>dsa.msc>Active Directory User and computer>Google.com(name of your domain) right click
>New>Group images is shown below
I have explained enough about the group now I will upload image of Group and type and Scopes I did not
explain about the Scopes yet but don't worry I will do it
I gave the name Security Group. On the left as you can see we have three scopes. 1: Domain Local 2:
Global 3: Universal . I will explain one by one and how to convert groups .
Domain Local Group:
Can contain users, computers, global groups and universal groups from
any domain in the forest and any trusted domain, and domain local groups
from the same domain. Can be a member of any domain local group in the
same domain.
Global Group:
can contain users, computers and groups from same domain but NOT
universal groups. Can be a member of global groups of the same domain,
domain local groups or universal groups of any domain in the forest or
trusted domains.
Universal Group:
can contain users and groups (global and universal) from any domain in
the forest. Universal groups do not care about trust. Universal groups
can be a member of domain local groups or other universal groups but
NOT global groups.
Apart from these groups you will see multiple built in Groups in Builtin container . when you install server on your machine and promote it as domain controller additional Groups are added . you must first learn about these groups and their rights so that when you are do lab exercises or in production environment you will
easily be able to discover if something is wrong for example log on issues and access resources in domain
and in forest. so let's see how many Built in security Groups do we have in a domain and what then can do.
when you go to Active Directory User and computers you see multiple container on the left pane. As you se
in image. All are by default security Group and on the right pane you can seen the name of the Group and
descriptions.
These are default Security Groups which have access and rights to perform specific task Before you add
any member to these group you must know the rights of that group so that you can be sure that you are going
to do right things. I will explain what rights they have by default.
Account Operator: Account Operator Group is the first Group in the list, by default it has no member if you add any member to this group that user will be able to add, delete, modify users , groups and computers located in Users and computer container and Organizational Unit in the Domain except from the Domain
controller Organizational Unit. This group does not have permission to make changes in Administrator group
and domain Admins Groups. Member of this Group can log on locally and shut down the Machine as they have given significant power in the domain.
Administrator: Administrator has the full control of all domain Controllers in the domain . Domain Admins
and Enterprise Admins are the member of this Group , Administrator Account is also default member of this
Administrator Group. If you add user to this group that user will be able to do whatever he/she wants. As
initially mentioned that the member of this group has full control. now you must be thinking what kind of
rights are given to member of Administrator group. so here are the rights they are given. Adjust memory quotas for a process; Back up files and directories; Bypass traverse checking; Change the system time; Create a pagefile; Debug programs; Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation; Force a shutdown from a remote system; Increase scheduling priority; Load and unload device drivers; Allow log on locally; Manage auditing and security log; Modify firmware environment values; Profile single process; Profile system performance; Remove computer from docking station; Restore files and directories; Shut down the system; Take ownership of files or other objects. I believe now you have the better understanding
about the rights which a user can have if you add him to this group.
Back up Operator : The member of this group are allowed to take the back up of file and directories as well as restore file and directories in domain Controller. Back up operator can also log on to the domain
controller and can shut down them so add user with caution as they have given significant power.
Print Operator : Member of Print Group manage ,add,delete and share printers connected to the domain Controllers in the domain. By default it has no member as the member of this group can load and unload device driver in domain controller. Be very careful before you add member to this group . Member of this Group can also log on locally and shut down the system.
Server Operator: Member of this Group log on interactively on domain Controller can add, delete shared
resources . can take back up and restore file they can start and stop some services , format hard disk and
shut down the Machine.
Remote Desktop User: Member of this Group can log on to domain controller remotely in the domain. By
default it has no member .
There are some other Groups too in built in container you can read about them , may be on the internet or in
the text book I mentioned only those group which have locally log on access . I explained about the Security Group which are in Built in Container. Now you need to know about the Group which are in Users container
before you learn about users group. let me explain about the Computer container which just below the Built in container . Computer container is for the computers when you join computer to domain it will go to that container however you can move your computers to specific Organizational Unit or Group. Its default computer container.
Domain Admins:Members of this group have full control of the domain. By default, this group is a member of the Administrators group on all domain controllers, all domain workstations, and all domain member servers at the time they are joined to the domain. By default, the Administrator account is a member of this group. Because the group has full control in the domain, add users with caution. If you talk about the ritghts
it has the same rights and can perform the same task as I mentioned in Administrator Group.
Domain Computer:This group contains all workstations and servers joined to the domain. By default, any computer account created becomes a member of this group automatically. by default it has no member
Domain Controllers: This group contains all domain controllers in the domain.
Domain User:
| This group contains all domain users. By default, any user account created in the domain becomes a member of this group automatically. This group can be used to represent all users in the domain. For example, if you want all domain users to have access to a printer, you can assign permissions for the printer to this group (or add the Domain Users group to a local group, on the print server, that has permissions for the printer). |
Enterprise Admins(appears only in forest root domain ):
you must remember this if your domain is the first domain in the forest that will be forest root domain and Enterprises Admins appears only in forest root
domain. Member of this Group exactly have the same rights and permission as Administrator do because of the membership so they also can do everything.
Schema Admins(Appears only in forest Root domain) :Members of this group can modify the Active Directory schema. By default, the Administrator account is a member of this group. By default it has no user.
Group Policy Creator Owner:Members of this group can modify Group Policy in the domain. By default, the Administrator account is a member of this group